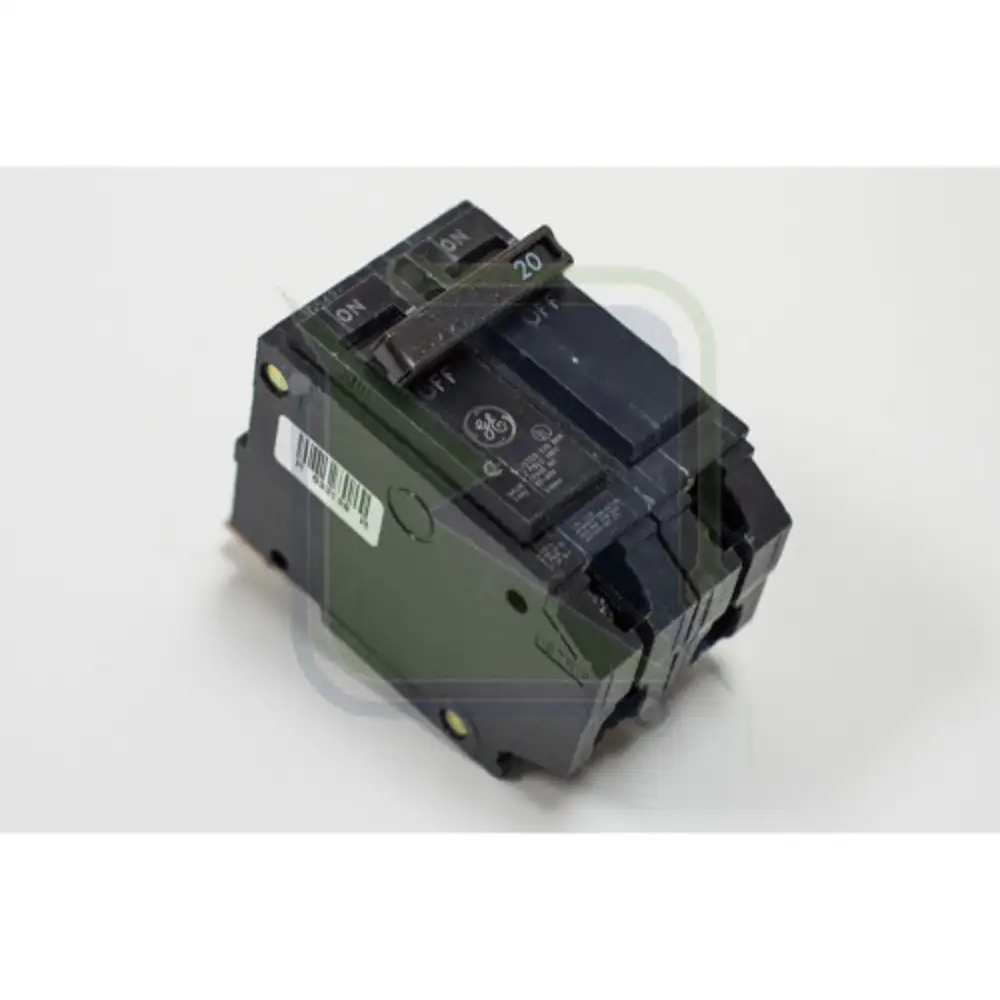
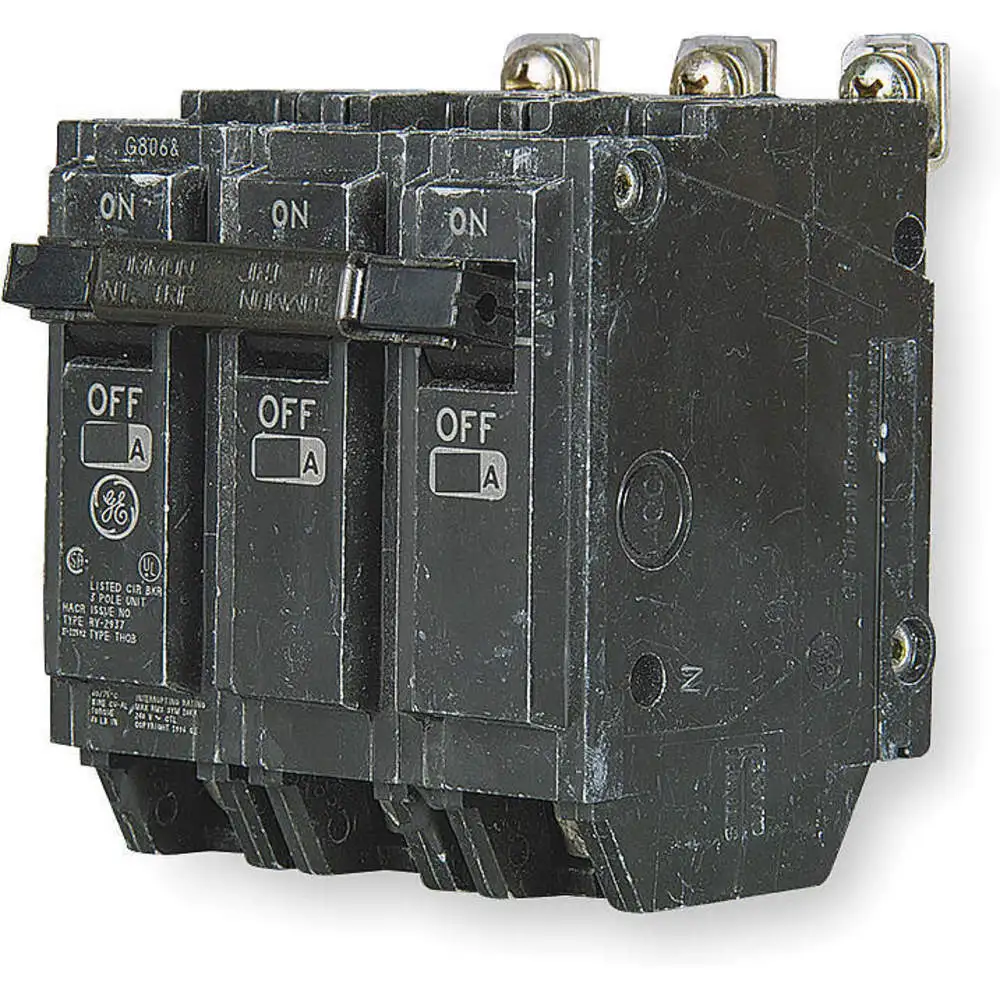
General Electric THQB32100 circuit breaker is used in electrical distribution systems to protect electrical circuits and equipment from overcurrents, short circuits and electrical faults. They are valuable in data centres, energy generation and power distribution applications.
Working Mechanism:
- Eaton thermal magnetic circuit breakers consist of a bimetallic strip that responds to the heat caused by excessive current flow and a solenoid-actuated plunger that responds to strong magnetic fields generated by high currents.
- When the current flowing through the circuit exceeds the rated capacity of the breaker, the bimetallic strip heats up and causes the breaker to trip.
- The magnetic element trips the breaker if it detects high magnetic fields.
- By stopping the current flow when the breaker trips, it safeguards the circuit from damage.
Features:
- General Electric THQB32100 circuit breaker features a thermal-magnetic trip mechanism to deliver long-time and instantaneous current limiting functions against faulty currents.
- It is integrated with a bolt-on mounting facility to minimise installation downtime in reverse-feed applications.
- This circuit breaker is rated at 240V and calibrated at an ambient temperature of 40 degrees C.
Compatible Accessories:
- General Electric EY3B Mounting Base: The brand's EY3B mounting base helps users to easily install this MCCB.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q. What is the difference between MCCBs and MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers)?
A. MCCBs are designed for higher current levels, whereas MCBs are used for lower current levels.
Q. Can I reset this General Electric THQB32100 circuit breaker after tripping?
A. Yes, you can manually reset it after a trip event, provided that the fault condition has been rectified and the circuit breaker is in 'off' position. Resetting the MCCB restores the contacts to the closed position, allowing the circuit to be energised again.
Q. What is the difference between a circuit breaker and a fuse?
A. A circuit breaker has an internal switch that trips when there is excess current, whereas a fuse is a metal piece that melts when excess current overloads the circuit.
 Change Country
Change Country
 In Stock : 540 Units
In Stock : 540 Units
